Running FastSpecFit¶
Note
Before running any of the examples below, we assume that you have
successfully installed and set up FastSpecFit.
Overview¶
The primary executable script for FastSpecFit is called fastspec, which
takes one or more Redrock redshift catalogs as input (and one or more
corresponding DESI spectra) and, by default, jointly models the DESI
spectrophotometry and broadband photometry.
Note that in addition to the Redrock catalog, fastspec also requires the
DESI coadded spectrum to be located in the same directory (with a default
coadd- prefix). In addition, there are two key support routines, which we
describe in more detail below:
fastqa, to build quality assurance (QA) figures; and
mpi-fastspecfit, to execute a variety of tasks (in parallel) on larger numbers of input files or catalogs.
One fastspec Example¶
To model the spectrum of a single object, we simply provide fastspec the
full path of an input Redrock catalog, the targetid of the object we are
interested in, and an (arbitrary) output filename:
$> fastspec $DESI_ROOT/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--targetids 39633345008634465 --outfile fastspec-example.fits
Click to view the informational output printed to the screen after executing this command.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:122:parse: /global/homes/i/ioannis/code/desihub/fastspecfit/bin/fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits --targetids 39633345008634465 --outfile fastspec-example.fits
INFO:io.py:525:select: Reading and parsing 1 unique redrockfile(s).
INFO:io.py:579:select: specprod=iron, coadd_type=healpix, survey=sv1, program=bright, healpix=7108
INFO:io.py:847:select: Gathered photometric metadata for 1 objects in 0.19 sec
INFO:io.py:937:read_and_unpack: Reading 1 spectrum from /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits
INFO:spectra.py:291:read_spectra: iotime 0.215 sec to read coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits at 2023-02-24T04:49:07.030436
INFO:io.py:966:read_and_unpack: Coadding across cameras took 0.01 seconds.
INFO:io.py:111:unpack_one_spectrum: Pre-processing object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465 z=0.368744].
INFO:fastspecfit.py:174:fastspec: Reading and unpacking 1 spectra to be fitted took 3.57 seconds.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:50:fastspec_one: Continuum- and emission-line fitting object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465, z=0.368744].
INFO:io.py:1505:cache_templates: Reading /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/science/gqp/templates/fastspecfit/1.0.0/ftemplates-chabrier-1.0.0.fits
INFO:continuum.py:1760:continuum_specfit: S/N_b=3.20, S/N_r=6.20, S/N_z=6.04, rest wavelength coverage=2630-7177 A.
INFO:continuum.py:1775:continuum_specfit: Fitting for the velocity dispersion took 1.44 seconds.
INFO:continuum.py:1790:continuum_specfit: Finding vdisp failed; adopting vdisp=125 km/s.
WARNING:continuum.py:1243:templates2data: Padding model spectrum due to insufficient wavelength coverage to synthesize photometry.
INFO:continuum.py:1857:continuum_specfit: Median aperture correction = 1.320 [1.209-1.471].
INFO:continuum.py:1884:continuum_specfit: Final fitting with 120 models took 0.38 seconds.
INFO:continuum.py:1918:continuum_specfit: Spectroscopic DN(4000)=0.944+/-0.028, Model Dn(4000)=1.101
INFO:continuum.py:1953:continuum_specfit: Smooth continuum correction: b=-0.252%, r=0.125%, z=0.036%
INFO:continuum.py:1978:continuum_specfit: Mstar=9.178 Msun, Mr=-19.80 mag, A(V)=0.542, Age=0.753 Gyr, SFR=3.535 Msun/yr, Z/Zsun=-0.473
INFO:continuum.py:2019:continuum_specfit: Continuum-fitting took 2.10 seconds.
INFO:emlines.py:2337:emline_specfit: Initial line-fitting with 28 free parameters took 0.35 seconds [niter=2, rchi2=1.5841].
INFO:emlines.py:2381:emline_specfit: Second (broad) line-fitting with 39 free parameters took 0.77 seconds [niter=3, rchi2=1.7877].
INFO:emlines.py:2386:emline_specfit: Chi2 with broad lines = 1.78772 and without broad lines = 1.58412 [chi2_narrow-chi2_broad=-0.20360]
INFO:emlines.py:2409:emline_specfit: Dropping broad-line model: delta-rchi2 -0.204<0.000.
INFO:emlines.py:2517:emline_specfit: Final line-fitting with 35 free parameters took 0.41 seconds [niter=2, rchi2=1.5550].
INFO:emlines.py:2608:emline_specfit: Dn(4000)=1.033 in the emission-line subtracted spectrum.
INFO:emlines.py:2649:emline_specfit: Emission-line fitting took 1.71 seconds.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:214:fastspec: Fitting 1 object(s) took 4.31 seconds.
INFO:io.py:1335:write_fastspecfit: Writing results for 1 object to fastspec-example.fits
INFO:io.py:1392:write_fastspecfit: Writing out took 1.38 seconds.
See the fastspec data model for a full description of
the contents of the fastspec-example.fits file which is written out. We can
visualize the results to create the
fastspec-sv1-bright-7108-39633345008634465.png file by invoking the
following command:
$> fastqa ./fastspec-example.fits --outdir ./
Click to view the informational output printed to the screen after executing this command.
INFO:fastqa:53:parse: /global/homes/i/ioannis/code/desihub/fastspecfit/bin/fastqa ./fastspec-example.fits --outdir ./
INFO:io.py:1716:read_fastspecfit: Read 1 object(s) from ./fastspec-example.fits
INFO:fastqa:131:main: Building QA for 1 objects.
INFO:io.py:665:select: Reading and parsing 1 unique redrockfile(s).
INFO:io.py:720:select: specprod=iron, coadd_type=healpix, survey=sv1, program=bright, healpix=7108
INFO:io.py:995:select: Gathered photometric metadata for 1 objects in 0.07 sec
INFO:io.py:1085:read_and_unpack: Reading 1 spectrum from /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits
INFO:spectra.py:291:read_spectra: iotime 0.470 sec to read coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits at 2023-03-31T14:14:14.983411
INFO:io.py:1114:read_and_unpack: Coadding across cameras took 0.01 seconds.
INFO:io.py:111:unpack_one_spectrum: Pre-processing object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465 z=0.368744].
INFO:fastspecfit.py:656:qa_fastspec: timeout 15 wget -q -o /dev/null -O ./tmp.fastspec-sv1-bright-7108-39633345008634465.jpeg "https://www.legacysurvey.org/viewer/jpeg-cutout?ra=105.48977452498902&dec=56.669300058331935&width=114&height=87&layer=ls-dr9"
INFO:fastspecfit.py:1342:qa_fastspec: Writing ./fastspec-sv1-bright-7108-39633345008634465.png
INFO:fastqa:241:main: QA for everything took: 12.64 sec
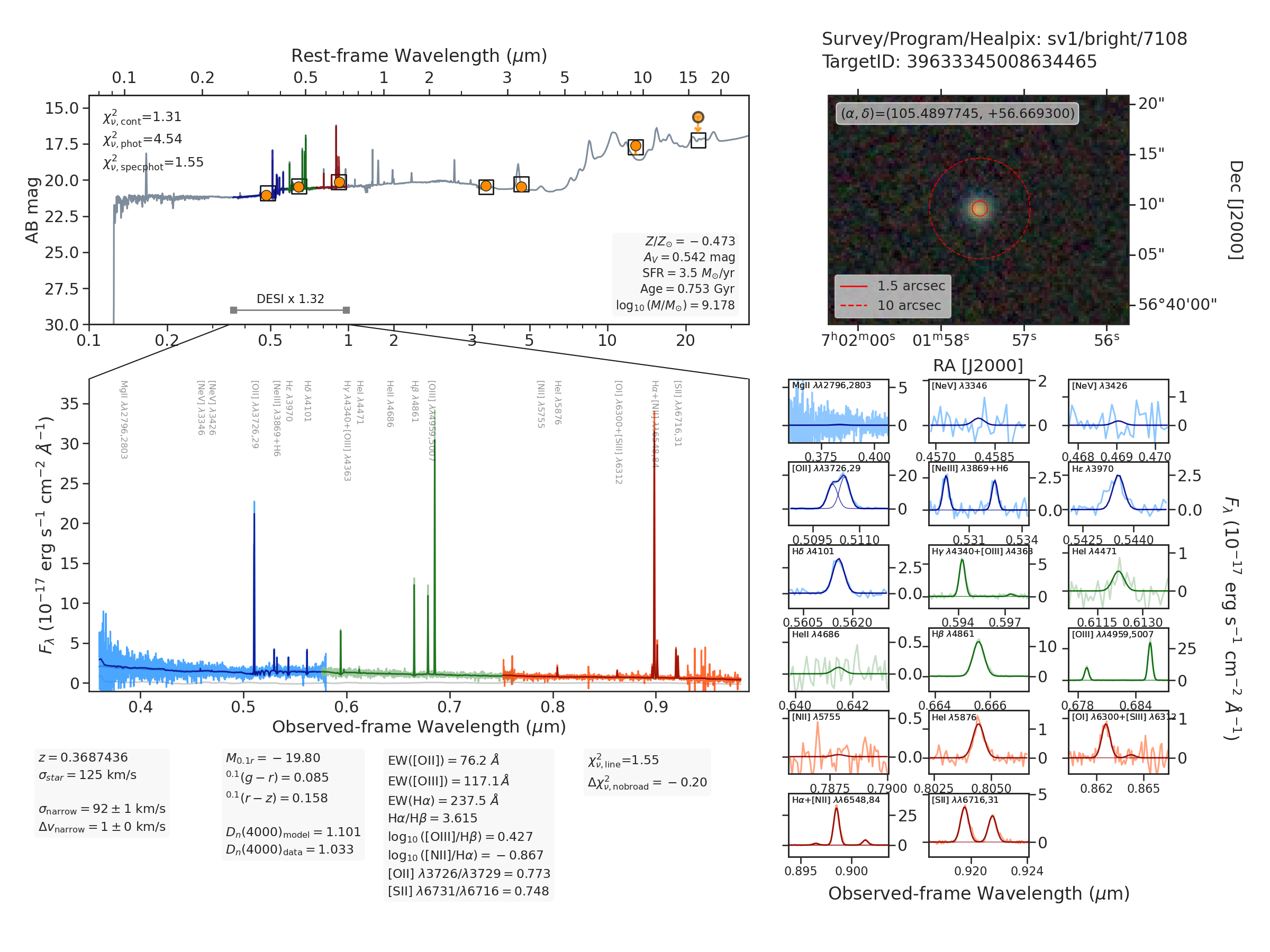
The figure above succinctly summarizes the fastspec inputs and modeling
results:
Upper-right panel: grz color cutout from the Legacy Surveys centered on the DESI target. The solid and dashed red circle represents the \(1.5^{"}\) diameter DESI fiber aperture and a \(10^{"}\) reference aperture, respectively.
Middle-left panel: Three-camera observed DESI spectrophotometry and best-fitting model, shown as light and dark blue, green, and red spectra, respectively, and spanning the observed-frame \(0.36-0.98~\mu m\) wavelength range. The thin, light gray curve around zero flux shows the smooth continuum correction which is added to the thick, dark gray best-fitting stellar population synthesis model (see the algorithms documentation for details).
Top-middle panel: Observed and modeled broadband spectral energy distribution between \(0.1-35~\mu m\) in the observed frame. The orange points (or arrows) show the observed grz (optical) and W1-W4 (infrared) fluxes or \(2\sigma\) upper limits from the Legacy Surveys, and the open square markers represent the photometry synthesized from the best-fitting model. The blue, green, and red spectra in this panel are the best-fitting DESI model after multiplying by the derived aperture correction (showin the bottom portion of the panel as the factor of 1.32).
Lower-right panel: Zoomed panels showing the data and best-fit model for all the emission lines within the observed spectral range.
In some cases it may be convenient to generate your own figure of the data and
the best-fitting models, which you can do by reading the data yourself and using
the spectra stored in the MODELS FITS extension:
import numpy as np
import fitsio
from astropy.table import Table
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from desiutil.dust import dust_transmission
from desispec.io import read_spectra
from desispec.coaddition import coadd_cameras
specfile = '/global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits'
fastfile = 'fastspec-example.fits'
meta = Table(fitsio.read(fastfile, 'METADATA'))
fast = Table(fitsio.read(fastfile, 'FASTSPEC'))
models, hdr = fitsio.read(fastfile, 'MODELS', header=True)
modelwave = hdr['CRVAL1'] + np.arange(hdr['NAXIS1']) * hdr['CDELT1']
spec = read_spectra(specfile).select(targets=meta['TARGETID'])
coadd_spec = coadd_cameras(spec)
bands = coadd_spec.bands[0]
mw_transmission_spec = dust_transmission(coadd_spec.wave[bands], meta['EBV'])
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True)
ax1.plot(coadd_spec.wave[bands], coadd_spec.flux[bands].flatten() / mw_transmission_spec,
color='gray', alpha=0.7, label='Data')
ax1.plot(modelwave, models[0, 0, :], label='Stellar Continuum Model', ls='-', color='blue')
ax1.plot(modelwave, models[0, 1, :], label='Smooth Continuum Correction', ls='--', color='k')
ax1.set_ylim(-2.5, 7.5)
ax1.legend(fontsize=8, loc='upper right')
ax2.plot(coadd_spec.wave[bands], coadd_spec.flux[bands].flatten() / mw_transmission_spec,
color='gray', alpha=0.7, label='Data')
ax2.plot(modelwave, np.sum(models, axis=1).flatten(), label='Final Model', ls='-', color='red')
ax2.legend(fontsize=8, loc='upper left')
ax2.set_xlabel(r'Observed-frame Wavelength ($\AA$)')
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.05, top=0.95, right=0.95)
fig.text(0.05, 0.5, r'Flux Density ($10^{-17}~{\rm erg}~{\rm s}^{-1}~{\rm cm}^{-2}~\AA^{-1}$)',
ha='center', va='center', rotation='vertical')
fig.savefig('fastspec-example.png')
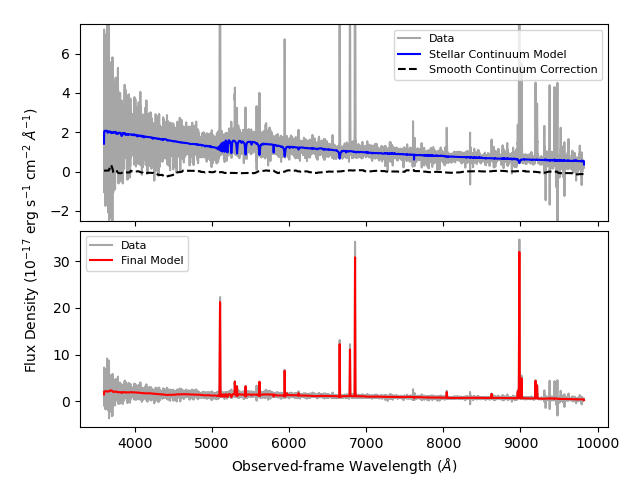
Note
All the quantities and models returned by FastSpecFit are measured from
DESI spectra which have been corrected for Galactic extinction, so the data
have to be extinction-corrected when generating the figure above.
One fastphot Example¶
FastSpecFit can also model the broadband photometry (at the given DESI
redshift) using fastphot. Using the same example object as above, we have:
$> fastphot $DESI_ROOT/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--targetids 39633345008634465 --outfile fastphot-example.fits
Click to view the informational output printed to the screen after executing this command.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:127:parse: /global/homes/i/ioannis/code/desihub/fastspecfit/bin/fastphot /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits --targetids 39633345008634465 --outfile fastphot-example.fits
INFO:io.py:665:select: Reading and parsing 1 unique redrockfile(s).
INFO:io.py:720:select: specprod=iron, coadd_type=healpix, survey=sv1, program=bright, healpix=7108
INFO:io.py:995:select: Gathered photometric metadata for 1 objects in 0.22 sec
INFO:io.py:1085:read_and_unpack: Reading 1 spectrum from /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits
INFO:io.py:111:unpack_one_spectrum: Pre-processing object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465 z=0.368744].
INFO:fastspecfit.py:194:fastspec: Reading and unpacking 1 spectra to be fitted took 3.22 seconds.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:51:fastspec_one: Continuum- and emission-line fitting object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465, z=0.368744].
INFO:continuum.py:1685:continuum_specfit: Adopting nominal vdisp=125 km/s.
WARNING:continuum.py:1243:templates2data: Padding model spectrum due to insufficient wavelength coverage to synthesize photometry.
INFO:continuum.py:1706:continuum_specfit: Fitting 120 models took 0.07 seconds.
INFO:continuum.py:1726:continuum_specfit: Model Dn(4000)=1.139.
INFO:continuum.py:1981:continuum_specfit: Mstar=9.528 Msun, Mr=-19.92 mag, A(V)=0.817, Age=1.679 Gyr, SFR=1.469 Msun/yr, Z/Zsun=-0.992
INFO:continuum.py:2022:continuum_specfit: Continuum-fitting took 0.20 seconds.
INFO:fastspecfit.py:236:fastspec: Fitting 1 object(s) took 0.86 seconds.
INFO:io.py:1759:write_fastspecfit: Writing results for 1 object to fastphot-example.fits
INFO:io.py:1816:write_fastspecfit: Writing out took 0.10 seconds.
And to generate the QA:
$> fastqa fastphot-example.fits --outdir ./
Click to view the informational output printed to the screen after executing this command.
INFO:fastqa:53:parse: /global/homes/i/ioannis/code/desihub/fastspecfit/bin/fastqa fastphot-example.fits --outdir ./
INFO:io.py:1716:read_fastspecfit: Read 1 object(s) from fastphot-example.fits
INFO:fastqa:131:main: Building QA for 1 objects.
INFO:io.py:665:select: Reading and parsing 1 unique redrockfile(s).
INFO:io.py:720:select: specprod=iron, coadd_type=healpix, survey=sv1, program=bright, healpix=7108
INFO:io.py:995:select: Gathered photometric metadata for 1 objects in 0.10 sec
INFO:io.py:1085:read_and_unpack: Reading 1 spectrum from /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/coadd-sv1-bright-7108.fits
INFO:io.py:111:unpack_one_spectrum: Pre-processing object 0 [targetid 39633345008634465 z=0.368744].
INFO:fastspecfit.py:656:qa_fastspec: timeout 15 wget -q -o /dev/null -O ./tmp.fastphot-sv1-bright-7108-39633345008634465.jpeg "https://www.legacysurvey.org/viewer/jpeg-cutout?ra=105.48977452498902&dec=56.669300058331935&width=114&height=87&layer=ls-dr9"
INFO:fastspecfit.py:1343:qa_fastspec: Writing ./fastphot-sv1-bright-7108-39633345008634465.png
INFO:fastqa:241:main: QA for everything took: 6.19 sec
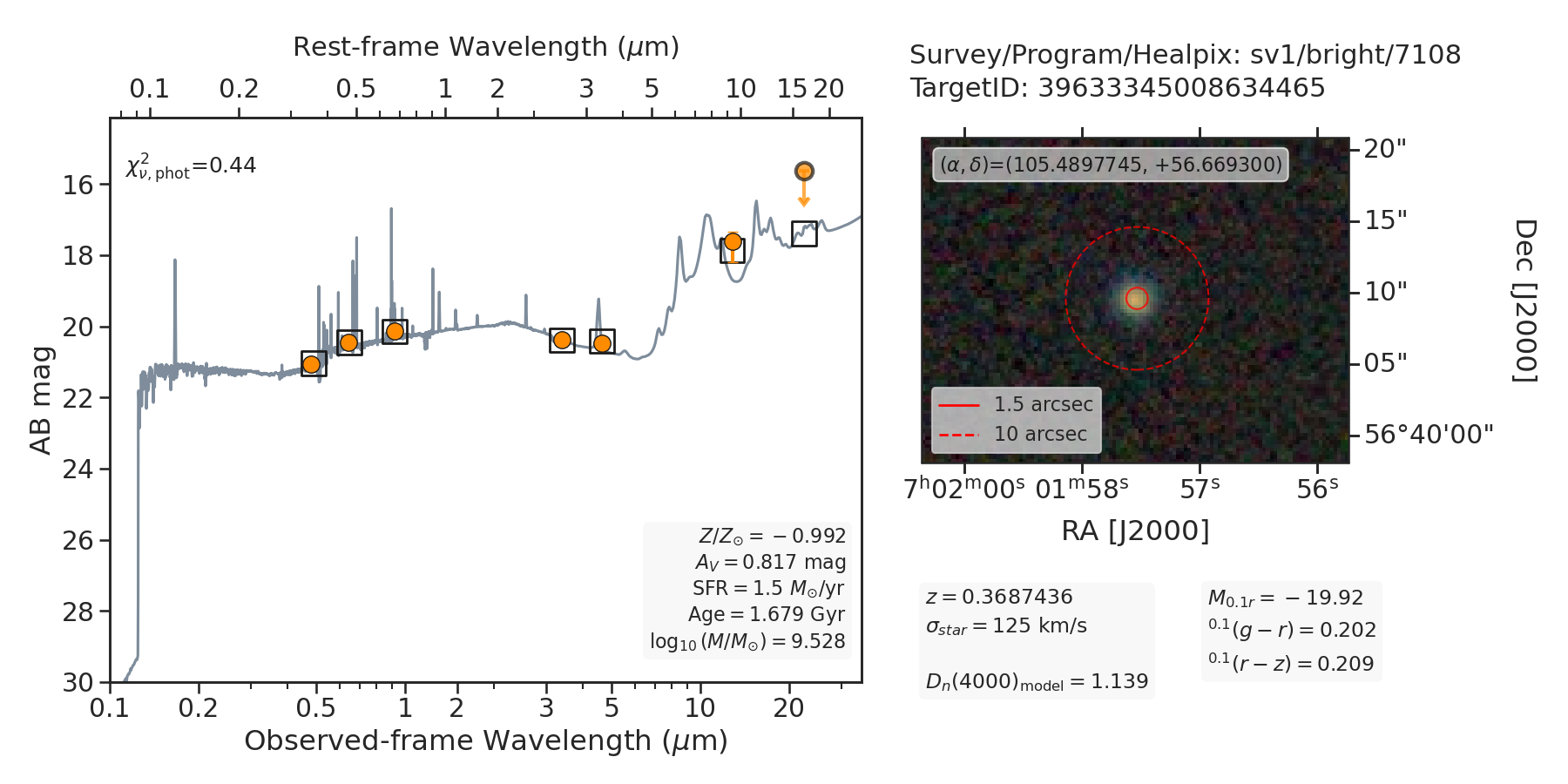
Once again, please refer to the fastphot data model
for a full description of the contents of the fastphot-example.fits file.
Note
As documented above, the orange points (or arrows) show the observed grz (optical) and W1-W4 (infrared) fluxes or \(2\sigma\) upper limits from the Legacy Surveys, and the open square markers represent the photometry synthesized from the best-fitting model.
More Examples¶
In the examples above, we selected one specific object using the --targetids
optional input, which can also be a comma-separated list. For example:
$> fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--targetids 39633345008634465,39633334917139798,39633348330522913 \
--outfile fastspec-example2.fits
Alternatively, you may want to fit a subset of the targets on this healpixel,
say the first 20 objects, in which case you would use the --ntargets keyword:
$> fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--ntargets 20 --outfile fastspec-example3.fits
If you don’t want to start at the zeroth object, you can offset by an integer
number of targets using the --firsttarget option, which in this example
would fit objects 50 through 70:
$> fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--firsttarget 50 --ntargets 20 --outfile fastspec-example4.fits
Finally, when fitting more than one object, you probably want to use
multiprocessing, so that multiple objects are fit simultaneously. We can use
parallelism (assuming you’re on a machine with more than one core) using the
--mp input:
$> fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits \
--firsttarget 50 --ntargets 20 --mp 20 --outfile fastspec-example5.fits
You can see all the options by calling either fastspec or fastphot with
the --help option, although most users will only invoke the options
documented above:
$> fastspec --help
usage: fastspec [-h] -o OUTFILE [--mp MP] [-n NTARGETS] [--firsttarget FIRSTTARGET] [--targetids TARGETIDS] [--no-broadlinefit] [--nophoto] [--percamera-models]
[--imf IMF] [--templateversion TEMPLATEVERSION] [--templates TEMPLATES] [--redrockfile-prefix REDROCKFILE_PREFIX]
[--specfile-prefix SPECFILE_PREFIX] [--qnfile-prefix QNFILE_PREFIX] [--mapdir MAPDIR] [--dr9dir DR9DIR] [--specproddir SPECPRODDIR] [--verbose]
[redrockfiles ...]
positional arguments:
redrockfiles Full path to input redrock file(s). (default: None)
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o OUTFILE, --outfile OUTFILE
Full path to output filename (required). (default: None)
--mp MP Number of multiprocessing threads per MPI rank. (default: 1)
-n NTARGETS, --ntargets NTARGETS
Number of targets to process in each file. (default: None)
--firsttarget FIRSTTARGET
Index of first object to to process in each file, zero-indexed. (default: 0)
--targetids TARGETIDS
Comma-separated list of TARGETIDs to process. (default: None)
--no-broadlinefit Do not allow for broad Balmer and Helium line-fitting. (default: True)
--nophoto Do not include the photometry in the model fitting. (default: False)
--percamera-models Return the per-camera (not coadded) model spectra. (default: False)
--imf IMF Initial mass function. (default: chabrier)
--templateversion TEMPLATEVERSION
Template version number. (default: 1.0.0)
--templates TEMPLATES
Optional full path and filename to the templates. (default: None)
--redrockfile-prefix REDROCKFILE_PREFIX
Prefix of the input Redrock file name(s). (default: redrock-)
--specfile-prefix SPECFILE_PREFIX
Prefix of the spectral file(s). (default: coadd-)
--qnfile-prefix QNFILE_PREFIX
Prefix of the QuasarNet afterburner file(s). (default: qso_qn-)
--mapdir MAPDIR Optional directory name for the dust maps. (default: None)
--dr9dir DR9DIR Optional directory name for the DR9 photometry. (default: None)
--specproddir SPECPRODDIR
Optional directory name for the spectroscopic production. (default: None)
--verbose Be verbose (for debugging purposes). (default: False)
What if you want to fit a particular survey, program, or healpixel. Do you
really need to specify the full path to each individual Redrock file? No!
FastSpecFit knows how the DESI data are organized, but to access this
information we need to use the higher-level mpi-fastspecfit script. For
example, to fit all the objects in the Iron spectroscopic production from
survey=sv, program=bright and healpix=7108, we would do (here, on a
single interactive Perlmutter node):
$> salloc -N 1 -C cpu -A desi -t 00:10:00 --qos interactive -L cfs
$> source /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/software/desi_environment.sh main
$> module load fastspecfit/main
$> export FASTSPECFIT_TEMPLATES=$DESI_ROOT/science/gqp/templates/SSP-CKC14z
$> time mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --survey sv1 --program bright \
--healpix 7108 --mp 128 --outdir-data .
$> ls -l ./iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv1 and program=bright
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 1/1 redrockfiles (left) to do.
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:46:run_fastspecfit: Planning took 0.16 sec
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:96:run_fastspecfit: Rank 0, ntargets=264: fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits -o ./iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/fastspec-sv1-bright-7108.fits --mp 128
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:119:run_fastspecfit: rank 0 done in 113.58 sec
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:140:run_fastspecfit: All done at Sun Aug 7 06:17:02 2022
real 1m55.770s
user 14m38.856s
sys 1m16.424s
total 12092
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ioannis ioannis 12007670 Aug 7 06:17 fastspec-sv1-bright-7108.fits
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ioannis ioannis 370424 Aug 7 06:17 fastspec-sv1-bright-7108.log
Since fitting can be relatively expensive (in this case, it took about two
minutes to fit 264 targets with 128 cores), you may want to see what’s going to
happen before fitting large numbers of objects, which we can do using the
--plan and/or --dry-run options:
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --survey sv1 --program bright \
--healpix 7108 --outdir-data . --plan
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv1 and program=bright
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 1/1 redrockfiles (left) to do.
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --survey sv1 --program bright \
--healpix 7108 --outdir-data . --dry-run
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv1 and program=bright
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 1/1 redrockfiles (left) to do.
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:46:run_fastspecfit: Planning took 0.01 sec
INFO:mpi-fastspecfit:96:run_fastspecfit: Rank 0, ntargets=264: fastspec /global/cfs/cdirs/desi/spectro/redux/iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/redrock-sv1-bright-7108.fits -o ./iron/healpix/sv1/bright/71/7108/fastspec-sv1-bright-7108.fits --mp 128
If you leave off any combination of the --survey, --program, and/or
--healpix options, the code will assume that you want all the possible
values of these keywords. For example, to see how many SV3 Redrock files would
need to be fit (not recommended without MPI parallelism!), one would do:
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --survey sv3 --outdir-data . --plan
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=bright
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=dark
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=other
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=backup
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 1023/1023 redrockfiles (left) to do.
INFO:mpi.py:326:plan: Skipping 70 files with no targets.
Note
One must always specify the spectroscopic production when calling
mpi-fastspecfit, in this case --specprod iron.
To fit the broadband photometry instead of the DESI spectroscopy, simply call
any of the examples in this section with the --fastphot option:
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --survey sv3 --outdir-data . --plan --fastphot
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=bright
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=dark
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=other
INFO:mpi.py:223:_findfiles: Building file list for survey=sv3 and program=backup
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 1023/1023 redrockfiles (left) to do.
INFO:mpi.py:326:plan: Skipping 70 files with no targets.
Finally, mpi-fastspecfit also knows about the tile-based cumulative,
per-night, and per-exposure coadds via the --coadd-type optional
input. For example:
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --coadd-type cumulative --tile 80613 --outdir-data . --plan
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 10/10 redrockfiles (left) to do.
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --coadd-type pernight --tile 80613 --outdir-data . --plan
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 57/57 redrockfiles (left) to do.
$> mpi-fastspecfit --specprod iron --coadd-type perexp --tile 80613 --outdir-data . --plan
INFO:mpi.py:309:plan: Found 283/283 redrockfiles (left) to do.